
Total Variance: Sum of the Variance Due to Noise and the Variance Of Systematic Random Sampling over all the sections sampled. If less than three sections are displayed, these values are not shown in the results.Īlthough this value depends to some degree upon the Variance Due to Noise, this dependency will normally be very small if the Variance Due to Noise is reasonably small. If this value is too high, more sections need to be sampled.Īt least three sections must be sampled for this value to be statistically meaningful. Ideally, this value will be both small and of roughly the same magnitude as the Variance Due to Noise. It is a primary contributor to the Total Variance. Variance of Systematic Random Sampling: Measure of the inter-sectional variance. If this value is too high, more sampling needs to be performed on each section. Ideally, this value will be both small and of roughly the same magnitude as the Variance Of Systematic Random Sampling. Variance Due to Noise: Formerly called the Nugget Variance, also known as the Nugget Effect, this is a measure of the intra-sectional variance.
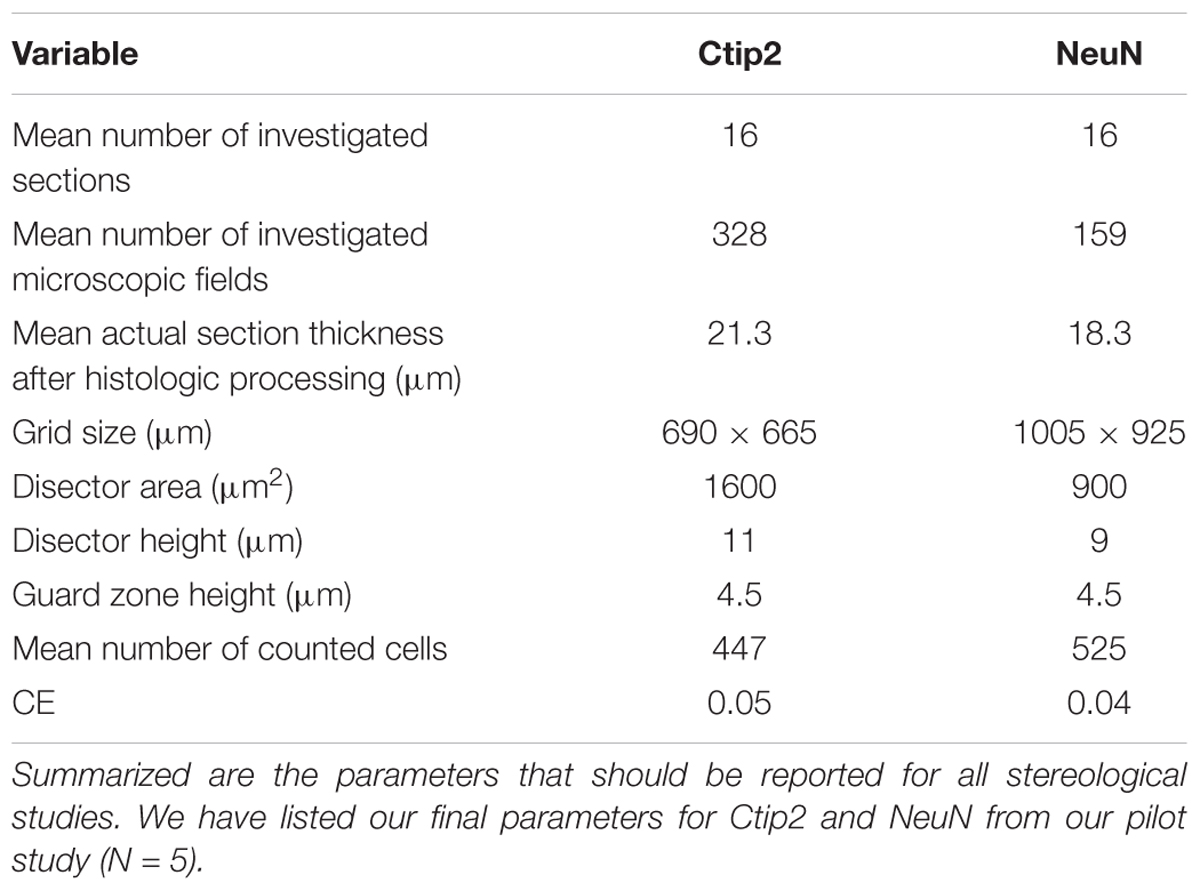
m=0 was used in the original CE calculations (Gundersen,1987).There are two values for many of the Gundersen categories:

This CE is only displayed if three or more sections are sampled.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
